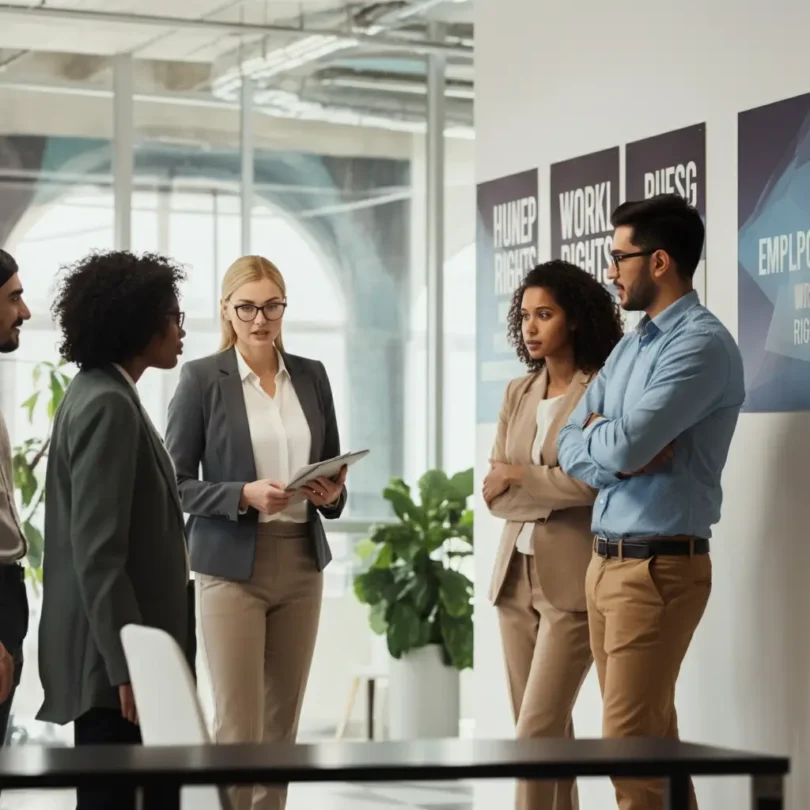
Understanding your rights as an employee is essential, whether you’re navigating your first job, managing a team, or running a business. Employment laws exist to create safe, fair, and equitable work environments, protecting both employees and employers. This guide breaks down employment law essentials, from discrimination policies to wage rules, helping you stay informed and compliant.
Dive in to explore the fundamental aspects of employment law, real-life examples of its impact, and tips to safeguard your workplace rights.
What is Employment Law?
Employment law is a set of regulations that governs the relationship between employers and employees. It ensures fairness in hiring, working conditions, compensation, and termination while protecting against discrimination, unsafe work practices, and exploitation. Every employee, whether working full-time, part-time, or under contract, has certain rights and protections under employment law.
By understanding these rights and the laws that protect them, both employers and employees can foster a workplace that is equitable and respectful.
Key Federal and State Employment Laws
Employment laws vary between federal and state jurisdictions. However, here are some key federal laws that every workforce participant should know:
- Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA): Establishes minimum wage, overtime pay, and youth employment standards.
- Civil Rights Act (Title VII): Prohibits employment discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
- Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA): Grants eligible employees unpaid leave for family or medical reasons, with job protection.
- Occupational Safety and Health Act (OSHA): Ensures workplace safety and health standards.
- Age Discrimination in Employment Act (ADEA): Protects employees aged 40 and older from discrimination.
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA): Ensures workplace accessibility and prohibits disability-based discrimination.
Each state has additional labor laws addressing aspects like sick leave, break times, and paid family leave. Make sure to review the specific laws in your state to stay compliant.
Understanding Discrimination and Harassment in the Workplace
Discrimination and harassment affect countless workers every year, often undermining morale and trust in the workplace. Here’s what you need to know:
What qualifies as discrimination?
Discrimination occurs when an employee is treated unfairly because of a characteristic protected under laws like the Civil Rights Act or the Equality Act. These protected characteristics include:
- Age
- Disability
- Gender reassignment
- Marital status
- Pregnancy or maternity
- Race
- Religion or belief
- Sex
- Sexual orientation
Discrimination may be direct (e.g., firing someone due to pregnancy) or indirect (e.g., imposing workplace policies that disadvantage a particular group).
Case Study:
A renowned tech company faced a $10 million lawsuit after male managers repeatedly overlooked women for leadership roles. Through legal action, the company altered its hiring practices and provided equal opportunities for growth, emphasizing the importance of knowing your rights.
If you feel you’ve been discriminated against, identify the type of discrimination, document evidence, and seek legal advice when necessary.
Wage and Hour Laws: Ensuring Fair Pay
Every employee deserves fair compensation for the work they do. Wage and hour laws, such as the FLSA, ensure:
- Minimum wage compliance: Rates vary between states but cannot fall below the federal minimum of $7.25/hour.
- Overtime pay requirements: Non-exempt employees must receive time-and-a-half pay for hours worked beyond 40 in a workweek.
- Proper classification of workers: Misclassifying employees as independent contractors can lead to wage theft.
Real-Life Example:
A chain of restaurants was penalized $2 million for denying overtime pay to eligible workers by misclassifying them as exempt employees. This highlights the financial and reputational risks of ignoring wage laws.
To ensure accurate payment, employees should keep track of hours worked and verify their paychecks.
Workplace Safety and Health Regulations
Workplace safety is a fundamental right. Under OSHA, employers are required to:
- Maintain hazard-free work environments.
- Provide protective gear and equipment.
- Inform employees about workplace risks.
Employees have the right to report unsafe conditions without fear of retaliation. For example, a factory worker who identified and reported toxic chemical exposure forced their employer to improve ventilation systems, preventing future harm.
Employers can conduct regular safety audits and training to stay compliant.
Employee Leave and Benefits: What You Should Know
Employees often juggle personal challenges alongside their professional responsibilities. The FMLA ensures eligible employees can take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave for:
- Personal medical issues
- Caring for a sick family member
- Bonding with a newborn or adopted child
Example Scenario:
A marketer took FMLA leave to care for her ailing father. The law protected her job during her absence, allowing her to return to the same role once her leave ended.
For shorter-term needs, state laws often mandate sick leave or include paid family leave programs.
Termination and Layoffs: Rights and Procedures
Job loss is stressful, but employees still have rights:
Unfair Dismissal Protections
Unlawful reasons for termination include discrimination, retaliation, or exposing safety violations. Employers must also follow fair termination procedures, such as providing notice as outlined in employment contracts.
Redundancy Pay
Employees with 2+ years of tenure in a company may qualify for redundancy pay. Length of service, age, and weekly wages are key factors in calculating redundancy compensation.
Case Spotlight:
A senior engineer used their knowledge of severance rights to negotiate a fair deal after a sudden layoff, ensuring financial stability.
If you suspect unfair termination, consult a labor lawyer or file a claim with the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
How to Resolve Employment Disputes
When workplace issues arise—whether it’s unpaid wages or harassment—here’s a process to follow:
- Document Everything: Collect emails, performance reviews, and pay stubs that support your claim.
- Speak Up Internally: Raise concerns with HR or your manager to seek resolution.
- Consult a Mediator: For disputes that escalate, mediators can help find an amicable solution.
- File a Formal Complaint: Pursue legal channels like the EEOC or a labor board if disputes remain unresolved.
Proactively addressing workplace challenges promotes transparency and resolution.
Resources for Employees and Employers
- U.S. Department of Labor (dol.gov): Access legal guidelines and worker protections.
- EEOC (eeoc.gov): File complaints related to workplace discrimination.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Groups like Workplace Fairness provide free resources and support for employees.
- Legal Assistance: Consult employment attorneys for complex issues.
Both employees and employers can benefit greatly from the accessibility of these resources, ensuring mutual understanding and compliance.
Protect Your Rights and Foster a Better Workplace
Employment laws exist to make workplaces safer, fairer, and more inclusive. By understanding the regulations that shape your rights as an employee or the responsibilities of an employer, you can foster a work environment where fairness and compliance thrive.
Need guidance? Research further, connect with advocacy organizations, or consult experts to empower yourself in the workplace.
Stay informed. Stay protected.